There are several ways to update your Google Pixel smartphone to the latest available patch or OS. If you’re willing to take matters into your own hands, you can skip the wait by sideloading an OTA update on your Google Pixel, and we will show you how.
Table of contents
- The difference between Android updates
- Download and install the Android SDK Platform-Tools package
- Enable USB debugging
- Download the latest OTA file for your device
- Boot your Pixel into Recovery mode
- Navigate to ADB sideload
- Connect your smartphone to a computer with ADB tools installed
- Enter the sideload command
- Reboot your phone
Luckily, the entire process is fairly simple. While many hardcore Android fans will know exactly what to do, not everyone is as adept at updating their phone. Firstly, there are a few differences in the kind of updates you can install on your Android phone.
The difference between Android updates
Monthly or regular updates are incremental, with full updates reserved for major releases – usually released just before the next new Pixel comes along. In this instance, an OTA or “over-the-air” update can be flashed relatively easily and will not restore any of your app or system settings when applied. To go back to a previous Android version, you will want a “factory” image. We have a dedicated guide on how to downgrade your Pixel, which explains this process:
- How to downgrade from Android 12 to Android 11 on Google Pixel [Video]
- How to downgrade from Android 13 back to Android 12 on Google Pixel [Video]
- How to downgrade from Android 14 back to Android 13 on Google Pixel [Video]
- How to downgrade from Android 15 back to Android 14 on Google Pixel [Video]
To recap, there are a few ways to get your Pixel updated to the latest official Google OTA update – you can wait until your phone gets a notification that will prompt you to download any waiting updates to your phone. This is normally the slowest method.
You can also force your smartphone to “pull” any waiting updates by heading to Settings > System > System update > Check for updates. This process is marginally faster and can be done as soon as an announcement confirms an update is available. However, like the OTA notification method, it can be a while before files are available.
The quickest method to get the latest update on your Google Pixel is to sideload the official OTA .zip file. Google offers several ways to do this, but both require access to a PC, Mac, or laptop.
It’s also worth noting that this process will work for almost all Android devices. You will need to obtain the official OTA files for your specific device manufacturer before attempting to sideload using this method. There may also be limitations on devices from manufacturers such as Xiaomi where an active SIM and on-device account has been active for a preset time period before sideloading is enabled.
Download and install the Android SDK Platform-Tools package
You’ll need to use ADB or Android Debug Bridge to sideload an OTA update on your Pixel. We recommend installing the unzipped platform-tools package on your desktop for quick access when running commands. You can download the latest platform-tools zip file from here. The Universal ADB Drivers from ClockWorkMod also make the process much easier if you are on a Windows machine compared to the drivers already on your machine.
Alternatively, Nexus Tools from Corbin Davenport offers a very simple way to ensure that you have the very latest version of Platform-Tools on your Windows, Mac or Linux machine at all times. Nexus Tools has been written in Dart, which can run on Linux, macOS, Windows, Windows Subsystem for Linux, and Chrome OS. Once Nexus Tools is finished, you can run adb, fastboot, and other commands with zero problems or issues.
Enable USB debugging
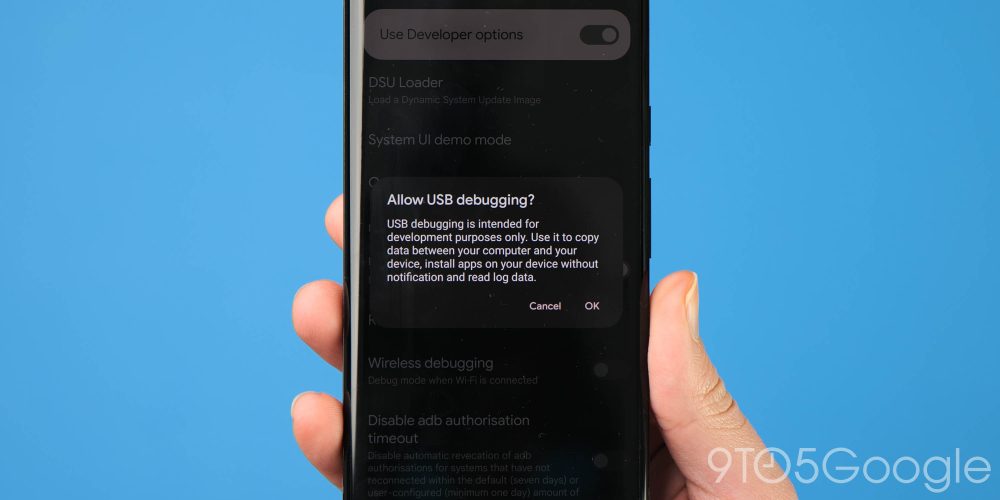
Firstly, ensure that you have Developer Options enabled on your Pixel. You can do that by heading to your device Settings > About phone, now tap “Build number” until a message confirms that you have Developer options enabled.
Now you need to head to Settings > System > Advanced > Developer options (you may need to expand a hidden menu for this). Scroll down to the “Debugging” section and tap the “Allow USB debugging” option. It’s also worth noting that if you want to downgrade again at any point, you may want to enable “OEM unlocking” but it is important to note that you can still sideload OTA updates on your Pixel without this option being enabled.
Download the latest OTA file for your device
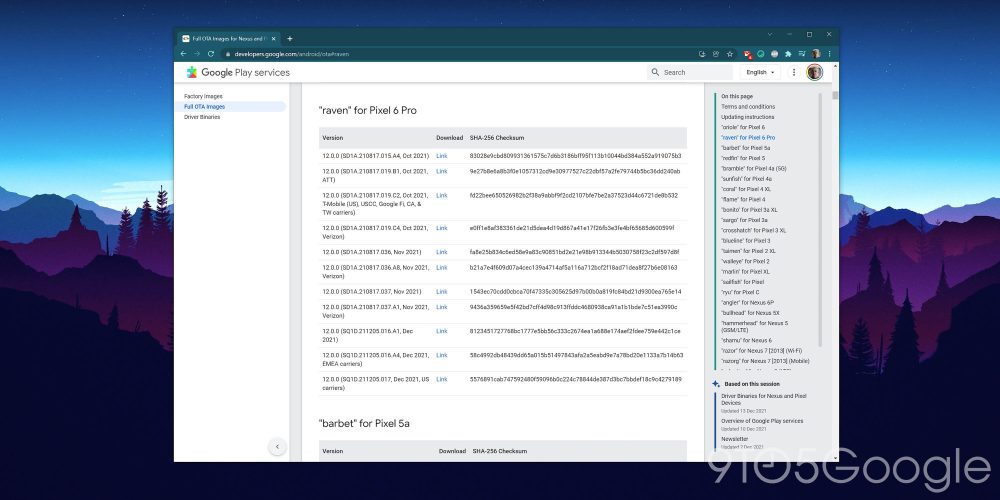
You’ll need a few things before you attempt to sideload an OTA file to your Google Pixel. Firstly, we need the latest OTA update available for your specific Pixel device. Google hosts the official builds for each Pixel on the dedicated developer site.
It is important to pick the right OTA file for your device, as this method will fail if you attempt to install the incorrect build for your device. The Made by Google smartphone line is guaranteed to get 3 full operating system upgrades with pre-Pixel 6 models given 4 years of security patches. As a result, many of Google’s Pixel series no longer receive official updates. You can see the currently supported hardware roadmaps below:
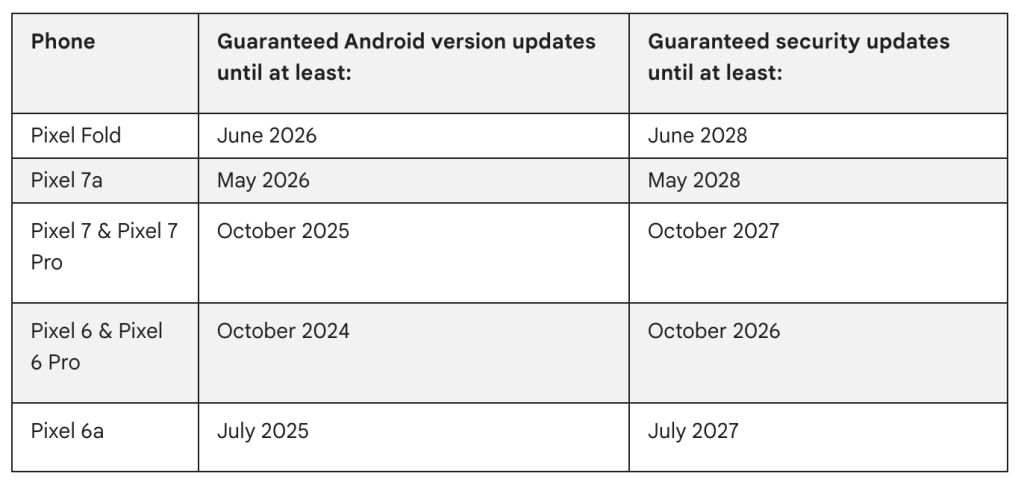
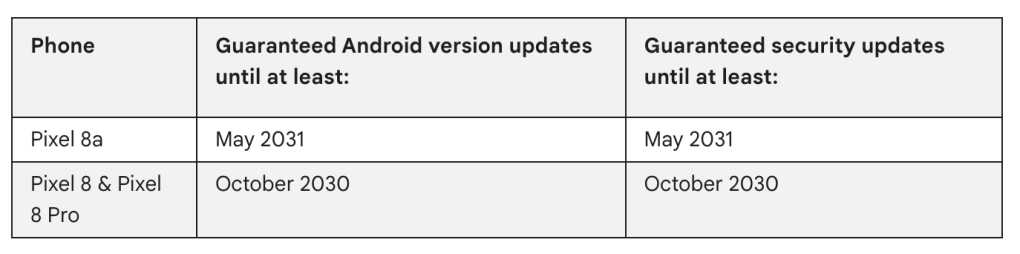
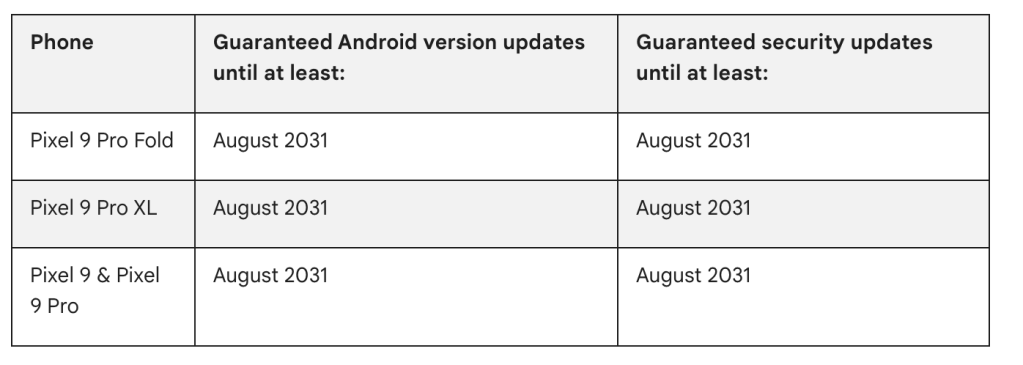
The Pixel 6 will stop getting “full” system updates from November 2024, but per the official update schedules a further two years of monthly patches are due. You can see just which device is no longer supported below:
- Google Pixel / Pixel XL (support ceased December 2019)
- Google Pixel 2 / Pixel 2 XL (support ceased December 2020)
- Google Pixel 3 / Pixel 3 XL (support ceased February 2022)
- Google Pixel 3a / 3a XL (support ceased September 2022)
- Google Pixel 4 / 4 XL (support ceased October 2022)
- Google Pixel 4a (support ceased November 2023)
- Google Pixel 4a 5G (support ceased November 2023)
- Google Pixel 5 (support ceased November 2023)
You can find OTA files required for the sideload process with appropriate dates and carrier-specific builds for every Google Pixel released right here. Alternatively, you can use the direct links for each device (with associated codenames) below:
- Google Pixel (“sailfish”)
- Google Pixel XL (“marlin”)
- Google Pixel 2 (“walleye”)
- Google Pixel 2 XL (“taimen”)
- Google Pixel 3 (“blueline”)
- Google Pixel 3 XL (“crosshatch”)
- Google Pixel 3a (“sargo”)
- Google Pixel 3a XL (“bonito”)
- Google Pixel 4 (“flame”)
- Google Pixel 4 XL (“coral”)
- Google Pixel 4a (“sunfish”)
- Google Pixel 4a 5G (“bramble”)
- Google Pixel 5 (“redfin”)
- Google Pixel 5a (“barbet”)
- Google Pixel 6 (“oriole”)
- Google Pixel 6 Pro (“raven”)
- Google Pixel 6a (“bluejay”)
- Google Pixel 7 (“panther”)
- Google Pixel 7 Pro (“cheetah”)
- Google Pixel 7a (“lynx”)
- Google Pixel Tablet (“tangorpro”)
- Google Pixel Fold (“felix”)
- Google Pixel 8 (“shiba”)
- Google Pixel 8 Pro (“husky”)
- Google Pixel 8a (“akita”)
- Google Pixel 9 (“tokay”)
- Google Pixel 9 Pro (“caiman”)
- Google Pixel 9 Pro XL (“komodo”)
- Google Pixel 9 Pro Fold (“comet”)
Please note: If regional builds exist for your device, it is important to sideload the correct OTA for your specific Google Pixel. Doing so ensures that you can access all features available within your global market. However, you can restore your device if you encounter or experience problems.
Boot your Pixel into Recovery mode
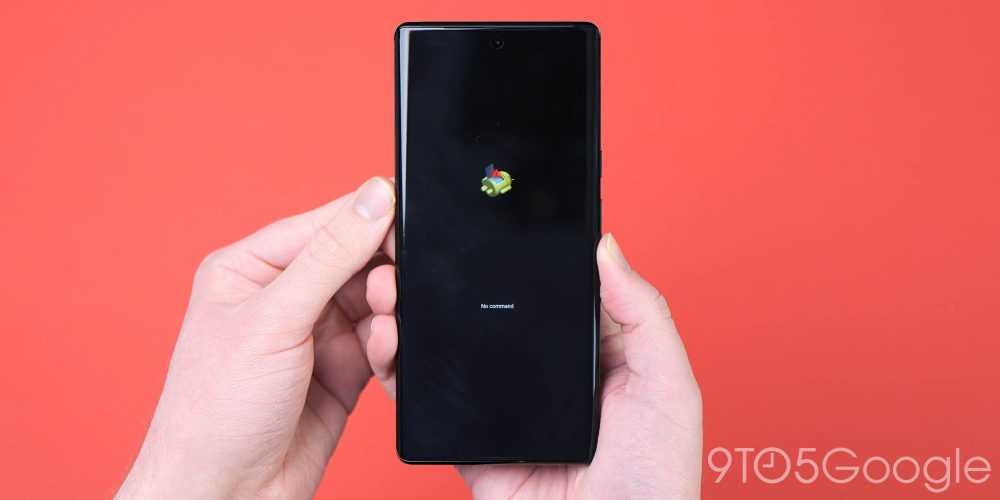

To initiate the process, you’ll need to boot your Pixel into Recovery mode, which enables the sideloading process. To access recovery mode, fully power down your phone. Then, hold down on the Power and Volume down buttons at the exact same time until you get to the Bootloader page.
Using the physical volume buttons to navigate, scroll down to Recovery mode. To select this option just click the power button. Alternatively, if you have your smartphone connected via USB-C to a computer, you can use the reboot recovery command or boot into the bootloader and use the volume keys to enter recovery mode:
Windows:
adb reboot bootloaderor Windows:
adb reboot recoveryMac:
./adb reboot bootloaderor Mac:
./adb reboot recovery
You should see a smaller Android lying down with an exclamation mark over it. When this screen is showing, press the Power button and the Volume up button for about a second to enter Recovery mode fully. Releasing the Volume up button will send you directly into Recovery mode.
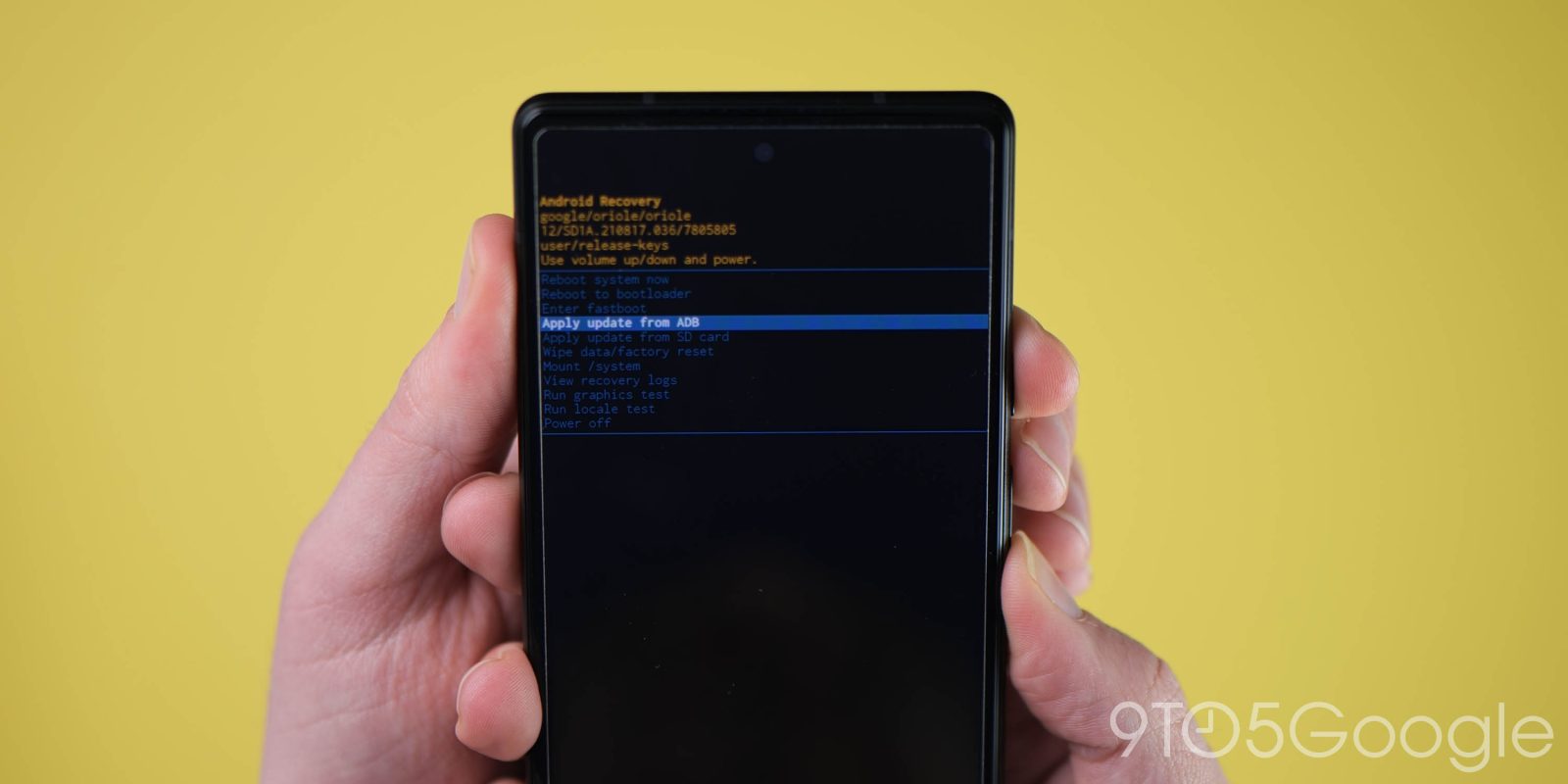
Navigate to ADB sideload
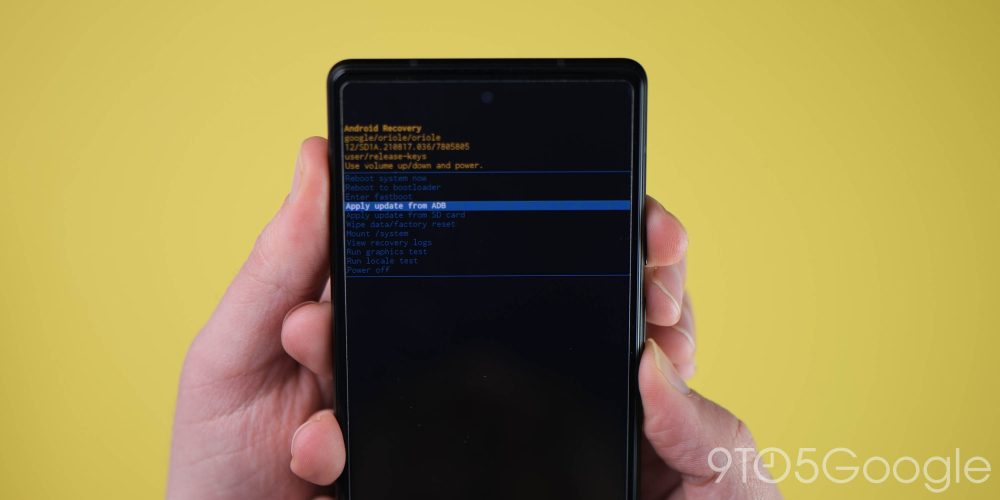
Using the volume buttons again, scroll down to “Apply update from ADB” and select this option using the power button. This will launch a mostly blank screen with text near the bottom directing you on how to sideload an OTA.
Connect your smartphone to a computer with ADB tools installed
Provided you have followed the early steps to install ADB tools on your computer and placed them in an easy-to-access folder or drive, then you can connect your smartphone to your computer if you have not already done so. You will need to open a Command Prompt or Terminal window within the directory or folder where you have saved the platform-tools file.
A quick method here is to locate the correct folder and type “cmd” into the address bar on Windows, or shift-click and tap “Open PowerShell window here”. PowerShell is effectively the same as Command Prompt, so don’t worry too much as it works just the same, but you’ll need to use the Mac-specific commands here.
If you are using a Mac and have placed the platform-tools folder on your desktop type: “./cd desktop” hit Enter and then “./cd platform-tools”. Alternatively, right-click on the unzipped folder location and select “New Terminal at Folder” to quickly open exactly where you need to be.
You sometimes need to replug in the USB-C cable on Mac as Mac OS after entering recovery as Macs sometimes will refuse to recognise your device until you do this.
To check if your Pixel is recognised and connected type the following and hit the “Enter” or “Return” key:
Windows:
adb devicesMac/Powershell:
./adb devices
Provided that you have connected your smartphone correctly, your device serial number will appear with other details to confirm it has been connected safely. You might see a prompt on your Pixel screen to “Allow USB debugging”. If you are using a trusted PC, toggle the “Always allow from this computer” for seamless future updates.
Enter the sideload command
As long as everything is in place, you can now sideload the OTA file. On Windows, ensure your Command Prompt is directed to the ADB tools folder and type in:
Windows:
adb sideloadMac/Powershell:
./adb sideload
You’ll then need to insert the file name of the original .zip folder you downloaded from Google and hit enter to start the OTA sideload process on your Pixel. If everything is working properly, you should see some dialog on your computer and handset that shows the sideload and installation process. This might take a while, and in some rare cases, the process can fail. If it does, just start the process again, as it can take multiple attempts for reasons we still don’t fully understand.
Note: Another simple method is to drag and drop the .zip folder into the Command Prompt or Terminal window after you have entered the sideload command. This ensures that you do not make typos or errors in the filename/structure. Hit the “Enter” or “Return” key, and this should initiate the sideloading process on your device.
Reboot your phone

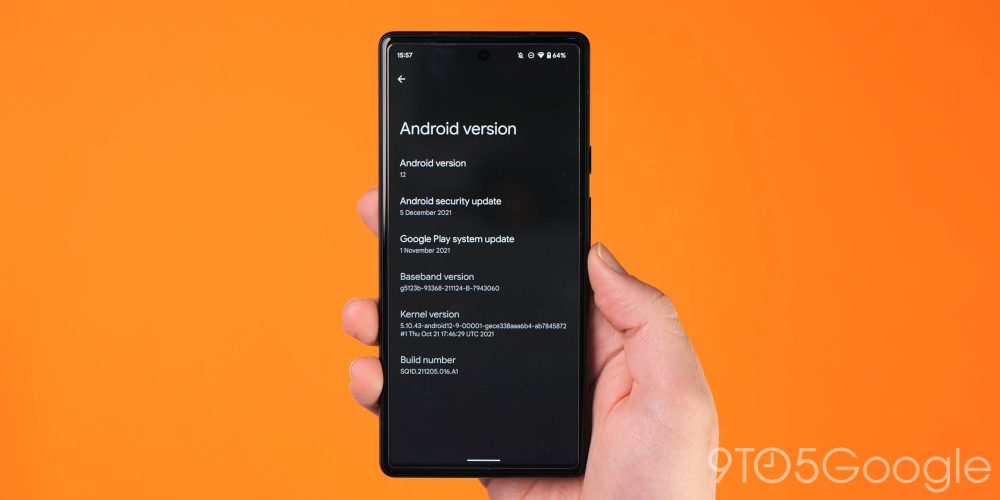
Once the OTA is done installing, you will be taken back to Recovery Mode. The last step to jump into the new update is to select the Reboot now option with your power button. Once your phone has rebooted, you should be safely updated with the very latest OTA.
A simple way to check if you have followed all of these steps correctly and sideload the OTA file is to head to Settings > About phone > Android version. This should be on the exact patch that you have sideloaded, indicating that you’ve successfully managed to complete the process.
Note: This process won’t wipe your device, but it’s good practice to back up any irreplaceable data in the rare case that something goes wrong.
If you have any questions, make sure to leave them in the comment section below.
FTC: We use income earning auto affiliate links. More.





Comments